Wood in moisture - wood equilibrium moisture content
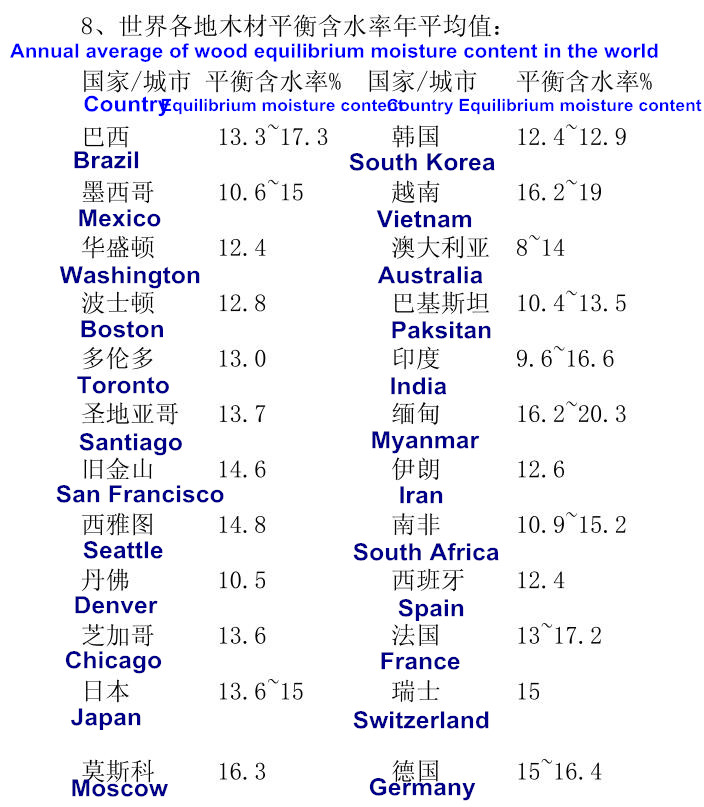
The equilibrium moisture content of wood is an issue that must be considered in formulating drying benchmarks, controlling and adjusting the drying process, controlling the size of dried wood and finished products in the warehouse, and formulating the final moisture content standards required for various wood products.
When the cell cavity contains no or very little free water, whenever the surrounding climate conditions (temperature, relative humidity or relative pressure of water vapor) change, the adsorbed water content in the wood cell wall also changes accordingly. If the water vapor partial pressure in the microcapillary system in the cell wall is greater than that in the air, the water vapor will move from the cell wall to the outside of the wood and evaporate into the atmosphere, reducing the absorbed water content. This phenomenon is called desorption. Conversely, if the water vapor partial pressure in the microcapillary system is smaller than that in the air, the water vapor will permeate from the air to the cell wall, that is, the wood will absorb moisture from the air, so that the absorbed water content will increase. This phenomenon is called hygroscopicity. The stable value of wood moisture content achieved in the desorption process is called desorption stable moisture content, and the stable value achieved in the moisture absorption process is called hygroscopic stable moisture content. The final stable moisture content of moisture absorption or desorption stable moisture content of thin wood in a certain air state is called the equilibrium moisture content. A piece of wood cannot be simultaneously affected by changes in climatic conditions along its entire thickness, so the surface of the wood reaches equilibrium moisture content before the interior.At a specified temperature, the moisture absorption of wood increases with the relative humidity of the air (that is, the relative pressure of water vapor in the air). When the relative humidity rises to close to 100%, the moisture absorption reaches the maximum value, and the equilibrium moisture content at this time is called the fiber saturation point. The fiber saturation point decreases with increasing temperature. For example, the fiber saturation point is about 30% at 0°C, 26% at 70°C, and 22% at 100°C. It is generally believed that the average fiber saturation point of various woods in our country is 30% at 20 °C. The stable moisture content reached by dry wood when it absorbs moisture is lower than that of wet wood when it desorbs under the same climatic conditions. This phenomenon is called hygroscopic hysteresis, or absorption hysteresis. The average hygroscopic hysteresis for many types of wood is approximately 2.5% over a relative humidity range of 60% to 90%. The hygroscopic hysteresis of thin wood and air-dried wood is very small, which can be ignored in production. High-temperature kiln-dried wood has a large hygroscopic hysteresis.
100 workers, 10000㎡ workshop, more than 20 years experience, ISO9001,CE certificated, two hour reach Xiamen port, this is how we keep superior quality and competitive offers for global valued customers.
Our main products cover Conventional Wood Drying Kilns,Track Type Veneer Drying Kilns,Heat Pump Drying Kilns ,wood carbonization kiln , thermol treatment drying kiln and so on.
If any product meed your demand, pls contact us for further information.




