Convective drying of wood in gaseous medium
When the moisture content is lower than the fiber saturation point
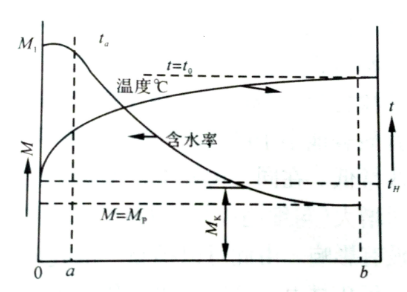
The drying curve of the drying process when the moisture content is lower than the fiber saturation point. During the preheating period (the oa section), the surface of the board hardly evaporates water, the moisture content does not change much, and the drying speed is equal to zero. Section ab represents the drying period, during which the moisture content of the surface layer decreases immediately after the process starts, resulting in a moisture content gradient, the moisture begins to move from the interior to the surface, and the moisture content of the entire section of the board also decreases. The drying rate starts quickly and approaches zero as the moisture content of the wood approaches the equilibrium moisture content.
The temperature of the wood reaches ta during the preheating period, continues to increase slowly during the drying period, and finally tends to the medium temperature. In fact, the drying process cannot be carried out until the moisture content of the wood reaches the equilibrium moisture content, but only to the specified moisture content, because it takes too long.
When the moisture content is higher than the fiber saturation point
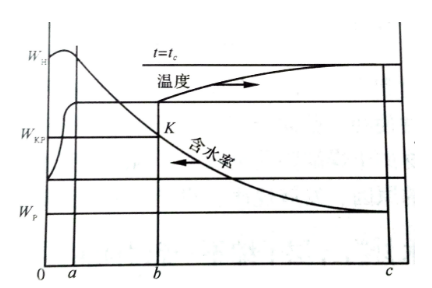
The drying curve of the drying process when the moisture content is higher than the fiber saturation point is divided into a constant speed drying period and a deceleration drying period in the drying period. During the isokinetic drying period, free water is evaporated from the surface of the wood, and the moisture content of the surface layer is maintained at a level close to the fiber saturation point. At this time, a sufficient amount of free water is supplied to the surface to evaporate, and the drying rate is fixed. During the deceleration drying period, the moisture content of the surface layer is lower than the fiber saturation point, the amount of water moving from the inner layer to the surface is less than the evaporation strength of the surface, the drying speed gradually slows down, and the drying speed gradually slows down to zero at the end of drying. Equilibrium moisture content.
The moisture content at the moment when the constant speed drying period ends and the deceleration drying period begins, is called the critical moisture content MKP. Due to the uneven distribution of moisture content across the wood thickness, the critical moisture content is often greater than the fiber saturation point. The more uneven the moisture content, the greater the MKP value. The increase in drying speed, thickness and density of the wood to be dried will cause the non-uniformity of moisture content along the thickness of the wood to increase during the drying process and increase the value of MKP. The higher the drying speed, the thicker and denser the dried wood, the closer the critical moisture content is to the initial moisture content, and the shorter the constant speed drying period. In the drying room, sawn timber of a certain size (thickness above 25mm) is often used for drying, and the constant speed drying period is practically non-existent.
Our main products cover Conventional Wood Drying Kilns,Track Type Veneer Drying Kilns,Heat Pump Drying Kilns,food drying chambers, heat treatment kiln and so on.If you are interested, welcome to contact me.




